Morton's Neuroma
A neuroma is a thickening of nerve tissue and can develop throughout the body. In the foot, the most common neuroma is a Morton’s neuroma; this typically forms between the third and fourth toes. The thickening of the nerve is typically caused by compression and irritation of the nerve; this thickening can in turn cause enlargement and, in some cases, nerve damage.
Neuromas can be caused by anything that causes compression or irritation of the nerve. A common cause is wearing shoes with tapered toe boxes or high heels that force the toes into the toe boxes. Physical activities that involve repeated pressure to the foot, such as running or basketball, can also create neuromas. Those with foot deformities, such as bunions, hammertoes, or flatfeet, are more likely to develop the condition.
Symptoms of Morton’s neuroma include tingling, burning, numbness, pain, and the feeling that either something is inside the ball of the foot or that something in one’s shoe or sock is bunched up. Symptoms typically begin gradually and can even go away temporarily by removing one’s shoes or massaging the foot. An increase in the intensity of symptoms correlates with the increasing growth of the neuroma.
Treatment for Morton’s neuroma can vary between patients and the severity of the condition. For mild to moderate cases, padding, icing, orthotics, activity modifications, shoe modifications, medications, and injection therapy may be suggested or prescribed. Patients who have not responded successfully to less invasive treatments may require surgery to properly treat their condition. The severity of your condition will determine the procedure performed and the length of recovery afterwards.
Causes and Symptoms of Foot Ulcers
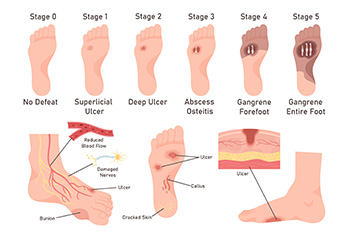
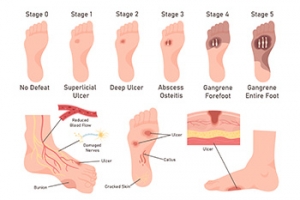
Foot ulcers are open sores that can range from a shallow surface wound to a deep crater that extends through skin layers, possibly reaching tendons and bones. Foot ulcers are especially common in diabetic patients or people with poor circulation, making them difficult to heal and prone to serious infections. Foot ulcers often develop due to nerve damage, or peripheral neuropathy, which causes a lack of sensation in the lower extremities. Another cause of foot ulcers is peripheral artery disease, which impedes blood flow and impairs the body’s ability to heal properly. This means that even minor injuries can go unnoticed, eventually leading to ulcers. Left untreated, foot ulcers can lead to infections, abscesses, and in extreme cases, gangrene, which might require amputation. Abnormal foot structures or wearing poorly fitting shoes can further contribute to the formation of such ulcers. If you have foot ulcers, it is suggested that you make a podiatrist a member of your healthcare team for regular monitoring and necessary treatment.
Diabetic foot care is important in preventing foot ailments such as ulcers. If you are suffering from diabetes or have any other concerns about your feet, contact one of our podiatrists from DeCaro Total Foot Care Center. Our doctors can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetes affects millions of people every year. The condition can damage blood vessels in many parts of the body, especially the feet. Because of this, taking care of your feet is essential if you have diabetes, and having a podiatrist help monitor your foot health is highly recommended.
The Importance of Caring for Your Feet
- Routinely inspect your feet for bruises or sores.
- Wear socks that fit your feet comfortably.
- Wear comfortable shoes that provide adequate support.
Patients with diabetes should have their doctor monitor their blood levels, as blood sugar levels play such a huge role in diabetic care. Monitoring these levels on a regular basis is highly advised.
It is always best to inform your healthcare professional of any concerns you may have regarding your feet, especially for diabetic patients. Early treatment and routine foot examinations are keys to maintaining proper health, especially because severe complications can arise if proper treatment is not applied.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our office located in West Hatfield, MA . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetes can cause two problems that can potentially affect the feet: Diabetic neuropathy and Peripheral Vascular Disease. Diabetic neuropathy occurs when nerves in your legs and feet become damaged, which prevents you from feeling heat, cold, or pain. The problem with diabetic neuropathy is that a cut or sore on the foot may go unnoticed and the cut may eventually become infected. This condition is also a main cause of foot ulcers. Additionally, Peripheral vascular disease also affects blood flow in the body. Poor blood flow will cause sores and cuts to take longer to heal. Infections that don’t heal do to poor blood flow can potentially cause ulcers or gangrene.
There are certain foot problems that are more commonly found in people with diabetes such as Athlete’s foot, calluses, corns, blisters, bunions, foot ulcers, ingrown toenails, and plantar warts. These conditions can lead to infection and serious complications such as amputation. Fortunately, proper foot care can help prevent these foot problems before they progress into more serious complications.
Each day you should wash your feet in warm water with a mild soap. When you finish washing your feet, dry them carefully especially between your toes. You should also perform daily foot inspections to ensure you don’t have any redness, blisters, or calluses. Furthermore, if you are diabetic, you should always wear closed-toed shoes or slippers to protect your feet. Practicing these tips will help ensure that your feet are kept healthy and away from infection.
If you have diabetes, contact your podiatrist if you have any of the following symptoms on your feet: changes in skin color, corns or calluses, open sores that are slow to heal, unusual and persistent odor, or changes in skin temperature. Your podiatrist will do a thorough examination of your feet to help treat these problematic conditions.
Wounds That Don't Heal Need to Be Checked
Common Foot Problems
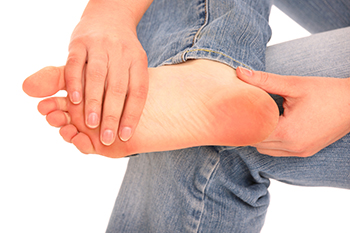
Foot pain can disrupt daily activities and impact overall well-being. Understanding common causes can help in managing and preventing discomfort. One frequent culprit is plantar fasciitis, which results from inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of the foot, often due to overuse or poor arch support. Another common source of foot pain is bunions, characterized by a bony bump at the base of the big toe, often made worse by tight or ill-fitting shoes. Arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can also lead to pain and stiffness in the joints of the feet. Additionally, conditions like flat feet or high arches can contribute to foot pain by causing uneven weight distribution. A podiatrist can identify and help you manage these issues. Sometimes simple preventive measures like wearing well-fitting shoes, using orthotic inserts, and stretching regularly can alleviate or even prevent your discomfort. If you have foot pain, it is suggested you consult a podiatrist for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Foot Pain
Foot pain can be extremely painful and debilitating. If you have a foot pain, consult with one of our podiatrists from DeCaro Total Foot Care Center. Our doctors will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
Causes
Foot pain is a very broad condition that could be caused by one or more ailments. The most common include:
- Bunions
- Hammertoes
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Bone Spurs
- Corns
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Ingrown Toenails
- Arthritis (such as Gout, Rheumatoid, and Osteoarthritis)
- Flat Feet
- Injury (from stress fractures, broken toe, foot, ankle, Achilles tendon ruptures, and sprains)
- And more
Diagnosis
To figure out the cause of foot pain, podiatrists utilize several different methods. This can range from simple visual inspections and sensation tests to X-rays and MRI scans. Prior medical history, family medical history, and any recent physical traumatic events will all be taken into consideration for a proper diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment depends upon the cause of the foot pain. Whether it is resting, staying off the foot, or having surgery; podiatrists have a number of treatment options available for foot pain.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in West Hatfield, MA . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Foot Pain
Our feet are arguably the most important parts of our bodies because they are responsible for getting us from place to place. However, we often don’t think about our feet until they begin to hurt. If you have pain in your feet, you need to first determine where on the foot you are experiencing it to get to the root of the problem. The most common areas to feel pain on the foot are the heel and the ankle.
Heel pain is most commonly attributed to a condition called plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia, which is the band of tough tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes becomes inflamed. Plantar fasciitis pain is usually worse in the morning, and it tends to go away throughout the day. If you have plantar fasciitis, you should rest your foot and do heel and foot muscles stretches. Wearing shoes with proper arch support and a cushioned sole has also been proven to be beneficial.
Some common symptoms of foot pain are redness, swelling, and stiffness. Foot pain can be dull or sharp depending on its underlying cause. Toe pain can also occur, and it is usually caused by gout, bunions, hammertoes, ingrown toenails, sprains, fractures, and corns.
If you have severe pain in your feet, you should immediately seek assistance from your podiatrist for treatment. Depending on the cause of your pain, your podiatrist may give you a variety of treatment options.
Common Foot Injuries From Running

Running frequently leads to foot injuries, including skin and toenail damage, plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia, and peroneal tendonitis. Skin conditions like blisters and calluses often arise from friction and improper footwear. Toenail damage, including bruised or ingrown nails, can occur from repetitive impact and tight shoes. Plantar fasciitis, characterized by heel pain and inflammation of the foot's connective tissue, is common among runners. Metatarsalgia causes pain in the ball of the foot due to overuse or poor arch support. Peroneal tendonitis results in pain along the outer side of the ankle from excessive strain. To manage these conditions, rest and appropriate treatment are essential. Wearing well-fitted, supportive shoes, using orthotic inserts, and incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises can help prevent and relieve these common running-related injuries. If you have endured a foot or ankle injury while running, it is suggested that you visit a podiatrist who can effectively treat your foot condition.
Sports related foot and ankle injuries require proper treatment before players can go back to their regular routines. For more information, contact one of our podiatrists of DeCaro Total Foot Care Center. Our doctors can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Sports Related Foot and Ankle Injuries
Foot and ankle injuries are a common occurrence when it comes to athletes of any sport. While many athletes dismiss the initial aches and pains, the truth is that ignoring potential foot and ankle injuries can lead to serious problems. As athletes continue to place pressure and strain the area further, a mild injury can turn into something as serious as a rupture and may lead to a permanent disability. There are many factors that contribute to sports related foot and ankle injuries, which include failure to warm up properly, not providing support or wearing bad footwear. Common injuries and conditions athletes face, including:
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fasciosis
- Achilles Tendinitis
- Achilles Tendon Rupture
- Ankle Sprains
Sports related injuries are commonly treated using the RICE method. This includes rest, applying ice to the injured area, compression and elevating the ankle. More serious sprains and injuries may require surgery, which could include arthroscopic and reconstructive surgery. Rehabilitation and therapy may also be required in order to get any recovering athlete to become fully functional again. Any unusual aches and pains an athlete sustains must be evaluated by a licensed, reputable medical professional.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our office located in West Hatfield, MA . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Sports Related Foot And Ankle Injuries
Foot and ankle injuries are common among people who participate in sports. Several factors contribute to this. They include failing to stretch or warm up properly, not wearing the proper type of shoe and not taping or providing other types of support for the ankle or foot. The most common foot and ankle injuries suffered by people involved in sports are plantar fasciitis, ankle sprains and Achilles tendon damage or ruptures. If not treated properly, they can lead to permanent disability.
Treating these injuries is relatively simple if they are identified and addressed early. Many athletes dismiss the initial aches and pains associated with injury as just soreness or tired muscles. Their first response is usually to try to work through it. This can lead to serious problems. Many minor injuries are made far more serious when athletes continue to put strain and pressure on them. That attitude can change a mild strain into a serious strain and a minor tear into a rupture. Athletes should have unusual aches and pains evaluated by a skilled medical professional.
Plantar fasciitis is a painful injury. It is inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue running from the heel to the base of the toes. If left untreated, it can lead to a degenerative disease called plantar fasciosis. There are several effective treatments for this ailment. Doctors often prescribe rest, massages, stretching, night splints, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medication, corticosteroids or surgery, usually in that order. The most effective treatment for plantar fasciitis is orthotics, which offers foot support. Surgery is occasionally used as a last resort, but it comes with the risk of nerve damage and infection and often does not stop the pain.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Running, jumping and walking all impact this tendon. Two common injuries to the Achilles tendon are tendonitis and a rupture of the tendon. Tendonitis is inflammation in the tendon often caused by an increase in the amount of stress placed on it. Non-surgical treatments include rest, ice or anti-inflammatory medication. A rupture (tear) of the Achilles tendon can be treated by placing the lower leg in a cast for several weeks or with surgery. Many physicians feel surgery is the better option because it lowers the risk of re-ruptures. Both methods require 4 to 6 months of rehabilitation.
Ankle sprains are the most common sports related foot and ankle injury. A sprain occurs when the ligament holding the ankle bones and joint stretches beyond its normal range. It can be treated non-surgically with a combination of rest, ice wrapped around the joint for 30 minutes immediately after injury, compression by a bandage and elevating the ankle above the heart for 48 hours. This combination is referred to as RICE. Severe ankle sprains in which the ligaments are torn may require reconstructive surgery followed by rehabilitation.
Bunion Deformities
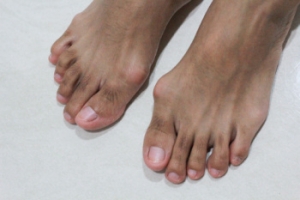
 A bunion, medically known as hallux valgus, is a deformity characterized by the misalignment of the big toe joint, causing the toe to lean toward the other toes and creating a noticeable bump on the side of the foot. This condition often results from a genetic predisposition, wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, high heels, or conditions such as arthritis. Symptoms of a bunion can include pain, swelling, redness surrounding the affected joint, and difficulty walking. Over time, the deformity can worsen, leading to increased discomfort and mobility issues. Conservative treatments for bunions include wearing wide-toed shoes, using protective pads to reduce friction, wearing orthotics, and taking mild pain relievers. If conservative methods fail to provide relief, more invasive options can include corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation or bunionectomy surgery to realign the bones, tendons, and ligaments. If you have a painful bunion, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
A bunion, medically known as hallux valgus, is a deformity characterized by the misalignment of the big toe joint, causing the toe to lean toward the other toes and creating a noticeable bump on the side of the foot. This condition often results from a genetic predisposition, wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, high heels, or conditions such as arthritis. Symptoms of a bunion can include pain, swelling, redness surrounding the affected joint, and difficulty walking. Over time, the deformity can worsen, leading to increased discomfort and mobility issues. Conservative treatments for bunions include wearing wide-toed shoes, using protective pads to reduce friction, wearing orthotics, and taking mild pain relievers. If conservative methods fail to provide relief, more invasive options can include corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation or bunionectomy surgery to realign the bones, tendons, and ligaments. If you have a painful bunion, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
If you are suffering from bunion pain, contact one of our podiatrists of DeCaro Total Foot Care Center. Our doctors can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
What Is a Bunion?
Bunions are painful bony bumps that usually develop on the inside of the foot at the joint of the big toe. As the deformity increases over time, it may become painful to walk and wear shoes. Women are more likely to exacerbate existing bunions since they often wear tight, narrow shoes that shift their toes together. Bunion pain can be relieved by wearing wider shoes with enough room for the toes.
Causes
- Genetics – some people inherit feet that are more prone to bunion development
- Inflammatory Conditions - rheumatoid arthritis and polio may cause bunion development
Symptoms
- Redness and inflammation
- Pain and tenderness
- Callus or corns on the bump
- Restricted motion in the big toe
In order to diagnose your bunion, your podiatrist may ask about your medical history, symptoms, and general health. Your doctor might also order an x-ray to take a closer look at your feet. Nonsurgical treatment options include orthotics, padding, icing, changes in footwear, and medication. If nonsurgical treatments don’t alleviate your bunion pain, surgery may be necessary.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office located in West Hatfield, MA . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Bunions
A bunion is an enlargement of the base joint of the toe that connects to the foot, often formed from a bony growth or a patch of swollen tissues. It is caused by the inward shifting of the bones in the big toe, toward the other toes of the foot. This shift can cause a serious amount of pain and discomfort. The area around the big toe can become inflamed, red, and painful.
Bunions are most commonly formed in people who are already genetically predisposed to them or other kinds of bone displacements. Existing bunions can be worsened by wearing improperly fitting shoes. Trying to cram your feet into high heels or running or walking in a way that causes too much stress on the feet can exacerbate bunion development. High heels not only push the big toe inward, but shift one's body weight and center of gravity towards the edge of the feet and toes, expediting bone displacement.
A podiatrist knowledgeable in foot structure and biomechanics will be able to quickly diagnose bunions. Bunions must be distinguished from gout or arthritic conditions, so blood tests may be necessary. The podiatrist may order a radiological exam to provide an image of the bone structure. If the x-ray demonstrates an enlargement of the joint near the base of the toe and a shifting toward the smaller toes, this is indicative of a bunion.
Wearing wider shoes can reduce pressure on the bunion and minimize pain, and high heeled shoes should be eliminated for a period of time. This may be enough to eliminate the pain associated with bunions; however, if pain persists, anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Severe pain may require an injection of steroids near the bunion. Orthotics for shoes may be prescribed which, by altering the pressure on the foot, can be helpful in reducing pain. These do not correct the problem; but by eliminating the pain, they can provide relief.
For cases that do not respond to these methods of treatment, surgery can be done to reposition the toe. A surgeon may do this by taking out a section of bone or by rearranging the ligaments and tendons in the toe to help keep it properly aligned. It may be necessary even after surgery to wear more comfortable shoes that avoid placing pressure on the toe, as the big toe may move back to its former orientation toward the smaller toes.